
Pictures of the Day
1-21-2026
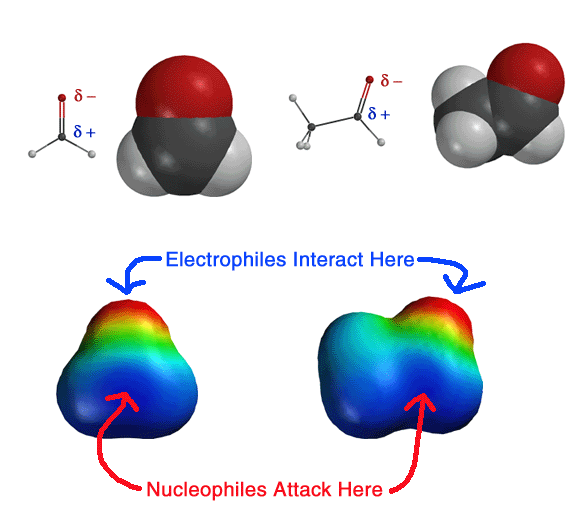
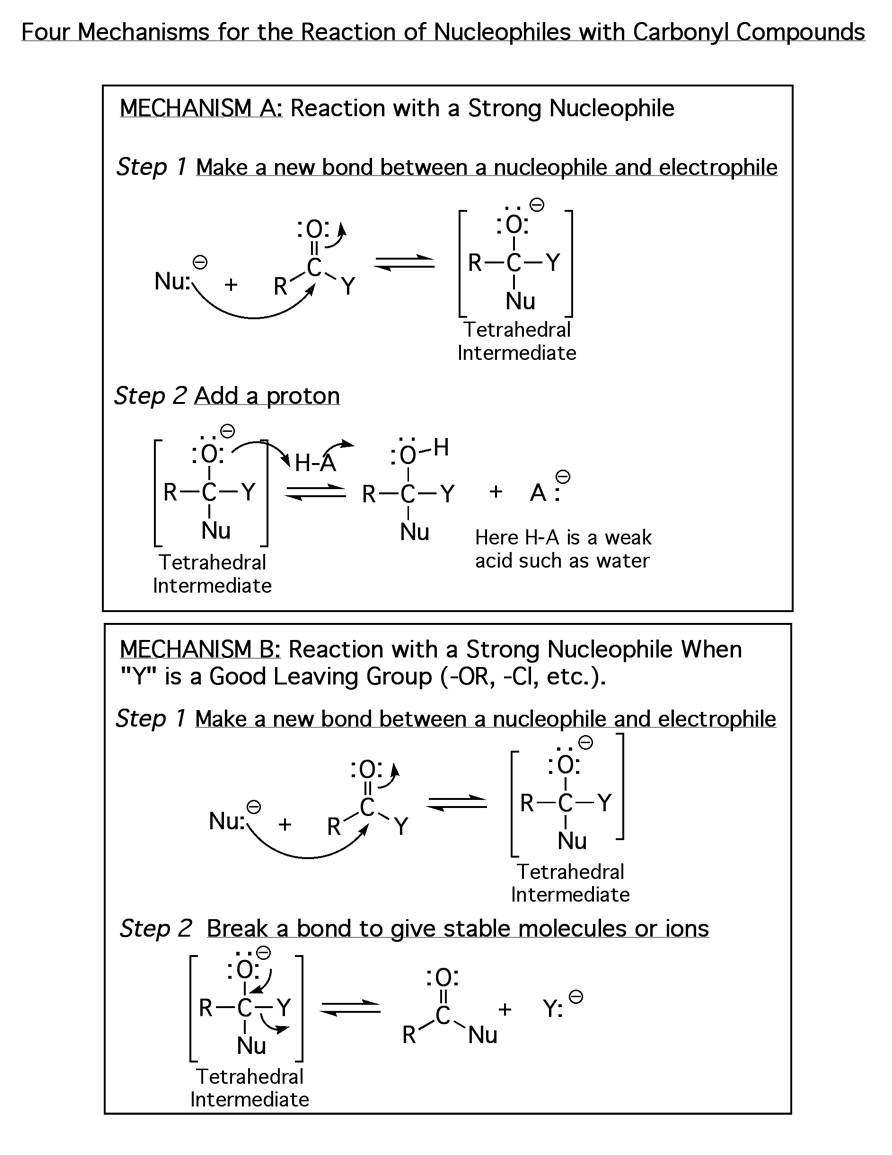
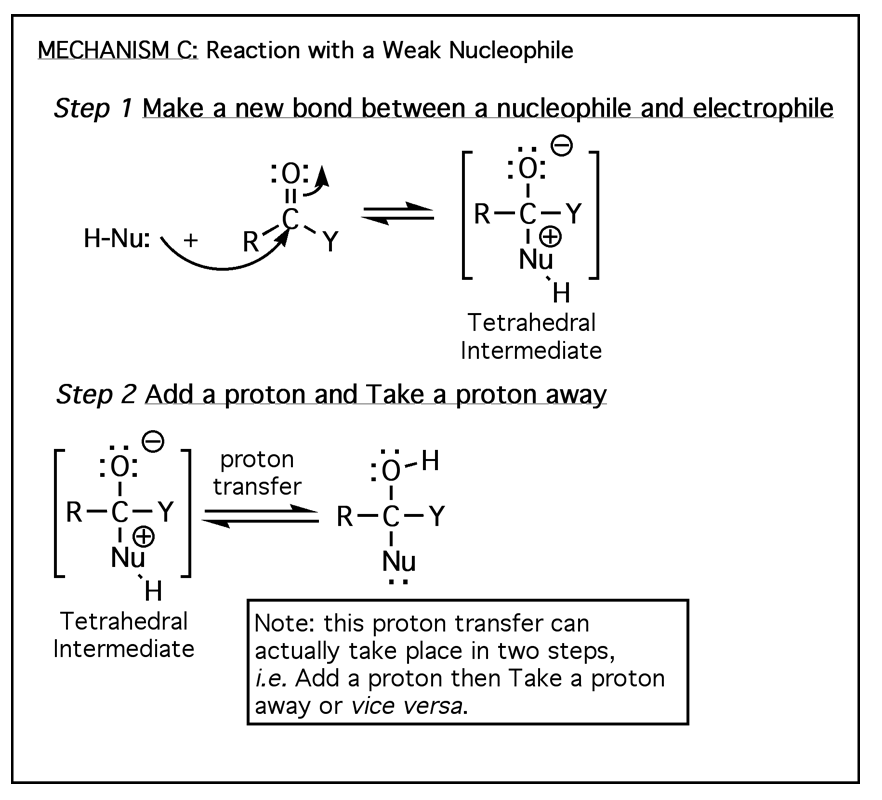
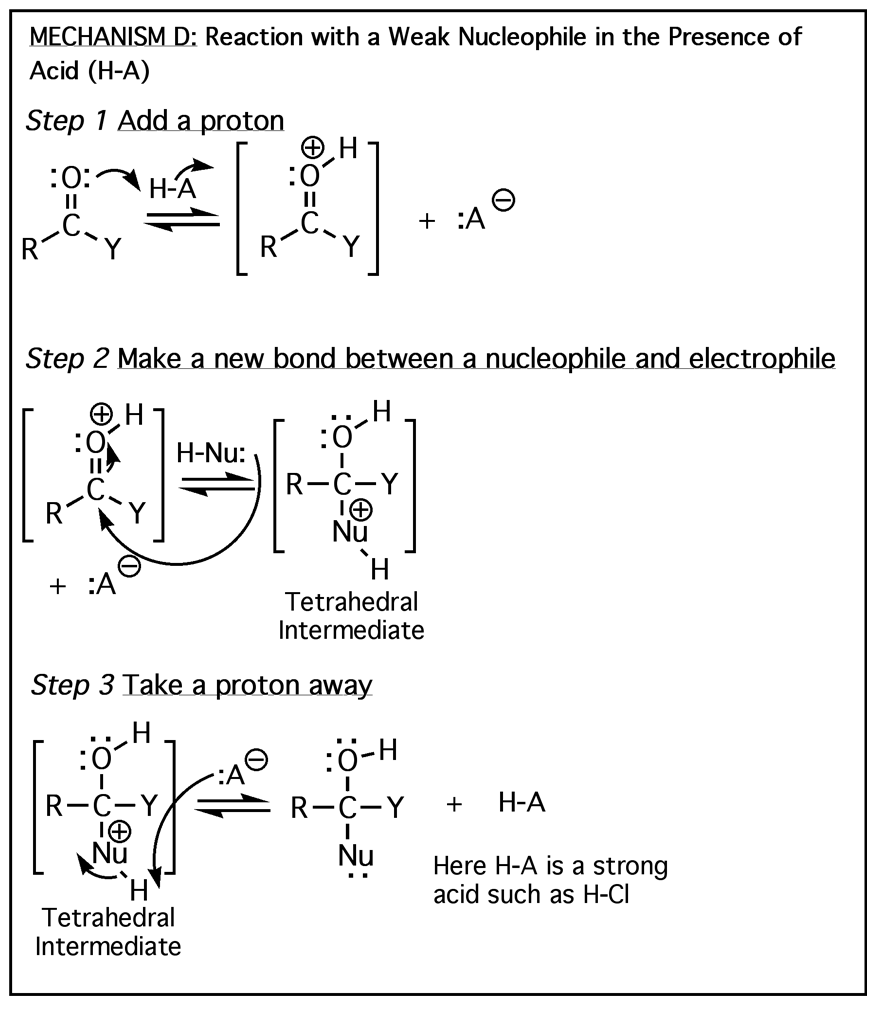
The above four mechanisms describe all of the different reactions you will see for carbonyl species such as aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acid derivatives. They are really just various combinations of the four mechanism elements 1) Make a newbond between a nucleophile and electrophile, 2) Break a bond so that realtively stable molecules or ions are formed, 3) Add a proton, and 4) Take a proton away.
All of the carbonyl mechanisms have a tetrahedral intermediate, and they all involve a nucleophile attacking the carbon atom of a carbonyl with simultaneous breaking of the C=O pi bond. The differences comes down to whether there is a leaving group involved and the timing of protonation/deprotonation.